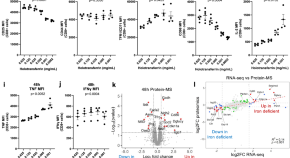
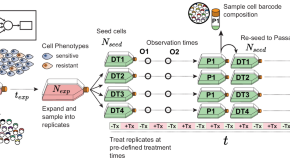
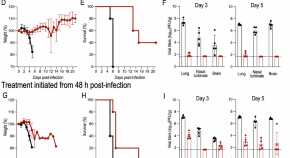
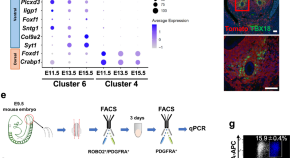
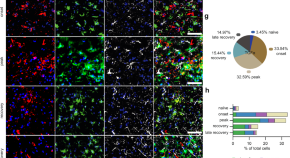
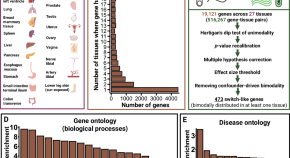
While switch-like expression (“on” in some individuals and “off” in others) has been linked to biological variation and disease susceptibility, a systematic analysis across tissues is lacking. Here, we analyze genomes, transcriptomes, and methylomes from 943 individuals across 27 tissues, identifying 473 switch-like genes. The identified switch-like genes are enriched for associations with cancers and immune, metabolic, and skin diseases. Only 40 (8.5%) switch-like genes show genetically hardwired on-versus-off expression in all tissues analyzed, i.e., universally switch-like expression. The remaining switch-like genes show on versus off expression only in specific tissues. Methylation analysis suggests that genetically driven epigenetic silencing explains the universal pattern, whereas hormone-driven epigenetic modification may underlie tissue-specific switch-like gene expression. Notably, tissue-specific switch-like genes tend to be switched on or off in unison within individuals, driven by tissue-specific master regulators. In the vagina, we identified seven concordantly switched off genes linked to vaginal atrophy. Experimental analysis of vaginal tissues shows that low estrogen levels lead to a decreased epithelial thickness and ALOX12 expression. We propose a model wherein switched off driver genes in basal and parabasal epithelia suppress cell proliferation, leading to epithelial thinning and vaginal atrophy. Our findings underscore the implications of switch-like genes for diagnostic and personalized therapeutic applications.
- Alber Aqil
- Yanyan Li
- Naoki Masuda